D-Day for digital security: On January 17, 2025, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) came into force to counter growing cyber threats. According to the Allianz Risk Barometer 2025, cyber threats pose the greatest risk to companies worldwide. With the resurgence of DDoS attacks, combined with the increased use of new technologies such as generative AI by cybercriminals and a global shortage of cybersecurity experts, the threat landscape is becoming more complex.
DORA aims to strengthen the digital resilience of financial institutions, better protect them against cyberattacks, and create common security standards across the EU. But what opportunities and challenges does DORA bring to German financial institutions?
Why is DORA Important for German Banks?
German financial institutions are seen as pioneers in security and compliance. With the implementation of DORA, they have the opportunity to further strengthen this leading position. The regulation offers many benefits:
- Increased cybersecurity: Strict IT security requirements ensure better protection against cyberattacks.
- More confidence: Customers and investors appreciate higher security standards, which can strengthen confidence in the German financial sector.
- Competitive advantage: Uniform regulations within the EU create a level playing field, allowing banks, for example, to make the best use of their expertise.
The five core requirements of DORA
The DORA framework is intended to strengthen the cybersecurity and resilience of the EU financial sector, and consists of five core requirements:
- Financial firms need robust ICT risk management, including strategies, policies and procedures to protect information, software and physical assets, combined with regular testing.
- Management, classification and reporting of ICT incidents: Firms must quickly report and resolve ICT-related incidents and cyber threats. Incidents must be reported within four hours and a detailed report must be provided within one week. Solid response plans and root cause analysis are essential.
- Digital operational resilience testing: ICT systems are regularly tested to assess vulnerabilities and the effectiveness of defenses.
- Third-party ICT risk management: Organizations need to actively manage risks from external service providers. This includes due diligence, audits, and clear contractual agreements. Third-party providers must also comply with DORA requirements.
- Information Sharing: Companies are encouraged to participate in voluntary information sharing to develop best practices. Privacy regulations must be observed.
By implementing these requirements, financial firms can strengthen their digital operational resilience and better respond to major disruptions.
Implementation Challenges
Despite the obvious benefits, there are challenges to implementing DORA:
- Skills shortage: Demand for IT security professionals far exceeds supply. Many banks struggle to find qualified staff.
- Complex requirements: The comprehensive DORA regulations require a significant investment of resources to be fully implemented.
- High costs: Implementing new security measures can be expensive.
Strategies for Successful Implementation
To address these challenges and take full advantage of the opportunities presented by DORA, financial institutions should adopt the following strategies:
- Invest in IT security: Increased budgets for security measures are essential.
- Employee training: Ongoing training ensures that employees can keep up with new requirements.
- Collaborative partnerships: Collaboration with other banks, IT service providers, and regulators can ease implementation.
- Leverage technology: Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation can help with risk assessment and compliance.
The Role of AI in DORA Compliance
Artificial intelligence offers promising solutions for efficiently meeting DORA requirements:
- Anomaly detection: AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data and identify conspicuous patterns that indicate potential security incidents.
- Process automation: Routine tasks, such as reviewing log files or generating reports, can be automated, thereby reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Streamline resilience testing: AI can help simulate cyberattacks and assess the resilience of systems.
By using AI in a targeted way, banks can strengthen their cyber resilience while making efficient use of resources.
Contact our experts and find out how your business can be protected with an automated security solution.
DORA’s Impact on Customers
In addition to impacting financial institutions themselves, DORA also brings benefits to customers:
- Greater privacy: Stricter security requirements ensure better protection of personal information from unauthorized access.
- More stable services: More robust IT systems ensure more reliable delivery of financial services.
- Increased trust: Improved cybersecurity increases customer confidence in the financial sector.
Conclusion
With DORA, the EU has taken a decisive step towards strengthening cybersecurity in the financial sector. The industry now has the opportunity to consolidate its leadership and benefit from common standards. However, implementation requires investment and a holistic cybersecurity strategy. With targeted measures and the use of modern technologies, German banks, for example, can overcome the challenges and further strengthen the trust of customers and investors. DORA is more than a regulation – it is a shield for the future of the financial sector.
DORA compliance requires not only robust strategies, but also the right technical protection against threats such as DDoS attacks. With our comprehensive DDoS protection, we can shield your IT infrastructure from overload attacks and ensure the continuous availability of your financial services – even under the highest loads.
Contact us anytime to strengthen your digital resilience and protect yourself from cyberattacks.
1.4 Tbps DDoS, Largest attack to date, successfully defended
In October 2024, Link11 was confronted with one of the largest DDoS attacks ever registered on the Link11 network. The attack reached peak values of 1.4 terabits per second (Tbps) and 120 million packets per second (Mpps). It was not based on sophisticated attack techniques, but on sheer volume. Despite the enormous load, the attack was successfully repelled in its entirety, and the customer’s services were maintained without interruption.
A look at the numbers: the sheer volume of the attack
DDoS attacks in Europe are becoming more frequent. Attacks of this size raise the question of how Europe can defend itself against DDoS attacks. As overall network capacity continues to grow, volumetric attacks remain popular to leverage this capacity.
A 1.4Tbps attack is the equivalent of streaming more than 300,000 HD videos simultaneously. Such a data flow overloads the network and server CPUs. Today, DDoS protection must be designed to be automatic and agile, as real-time responses are necessary and manual intervention or pure filter solutions are no longer sufficient for large amounts of data.
Attack details: A complex strategy
The DDoS attack used a variety of attack vectors, making the defense measures significantly more difficult. The attack source had a total of 859,756 unique IP addresses, indicating a high degree of distribution among attack sources. It can be assumed that many compromised devices worldwide were involved in the attack. This distribution is typical for modern DDoS attacks, in which cybercriminals often use botnets of IoT devices or insecure home routers. Here, the US was the main source of traffic, followed by China.
Traffic split by countries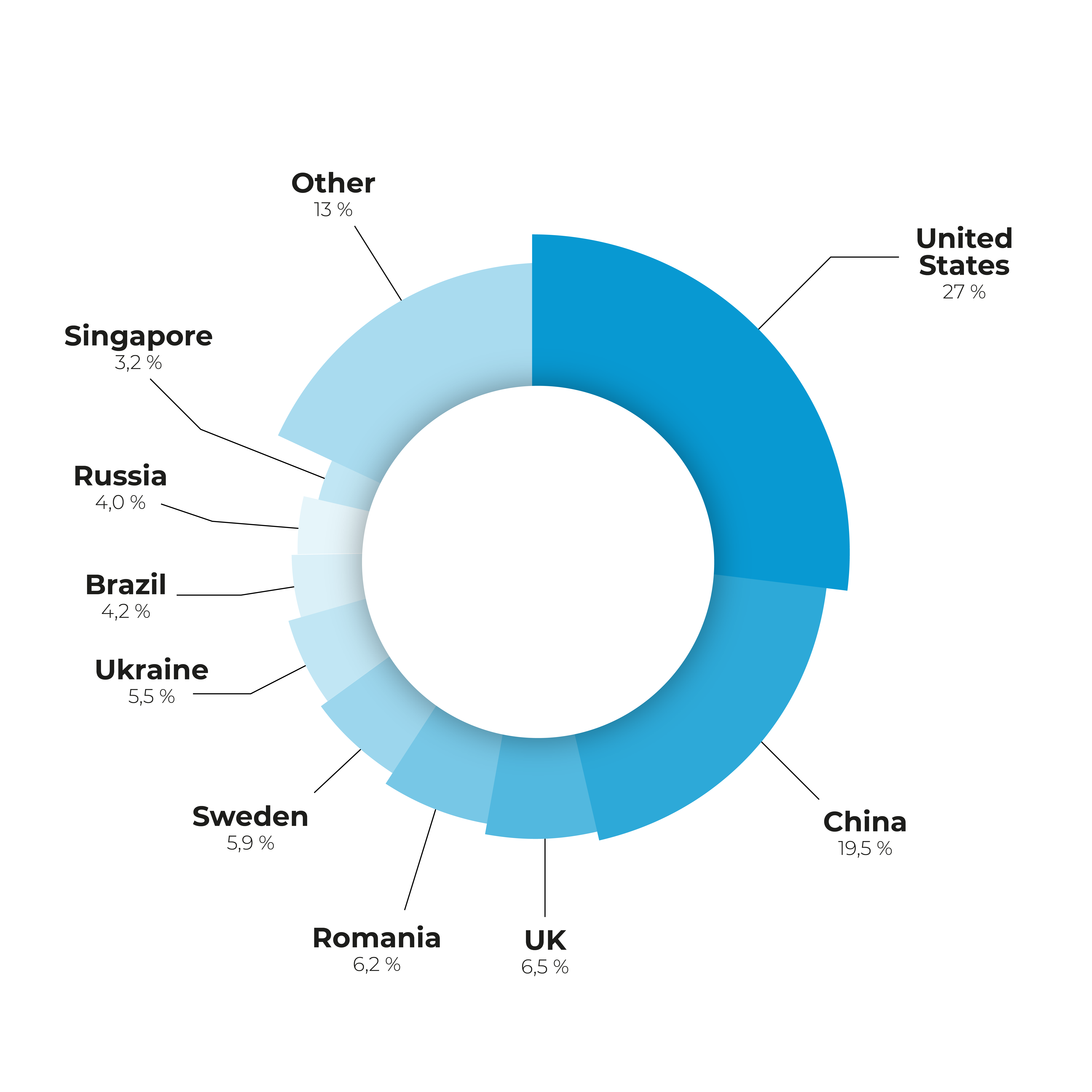
The breakdown of attack vectors is as follows:
- TCP (over 50% of the total attack volume): The use of randomly selected source ports and the targeting of destination port 80 (HTTP) suggests that the attackers were attempting to directly overload the targets web services.
- UDP (almost 40% of the volume): Since UDP packets are usually not connection-oriented, they are particularly suitable for attacks. They can be sent quickly and in large quantities without the need for a prior connection.
- ICMP accounts for about five percent of the attack volume. ICMP packets can be used to detect network connections, which suggests that the attackers may be trying to overload the network infrastructure.
- GRE: (around 5% of the volume): GRE tunnels are often used to transfer data over VPNs. This suggests that the attackers were attempting to disguise the GRE packets as a legitimate service and bypass filters and make their attacks more effective.
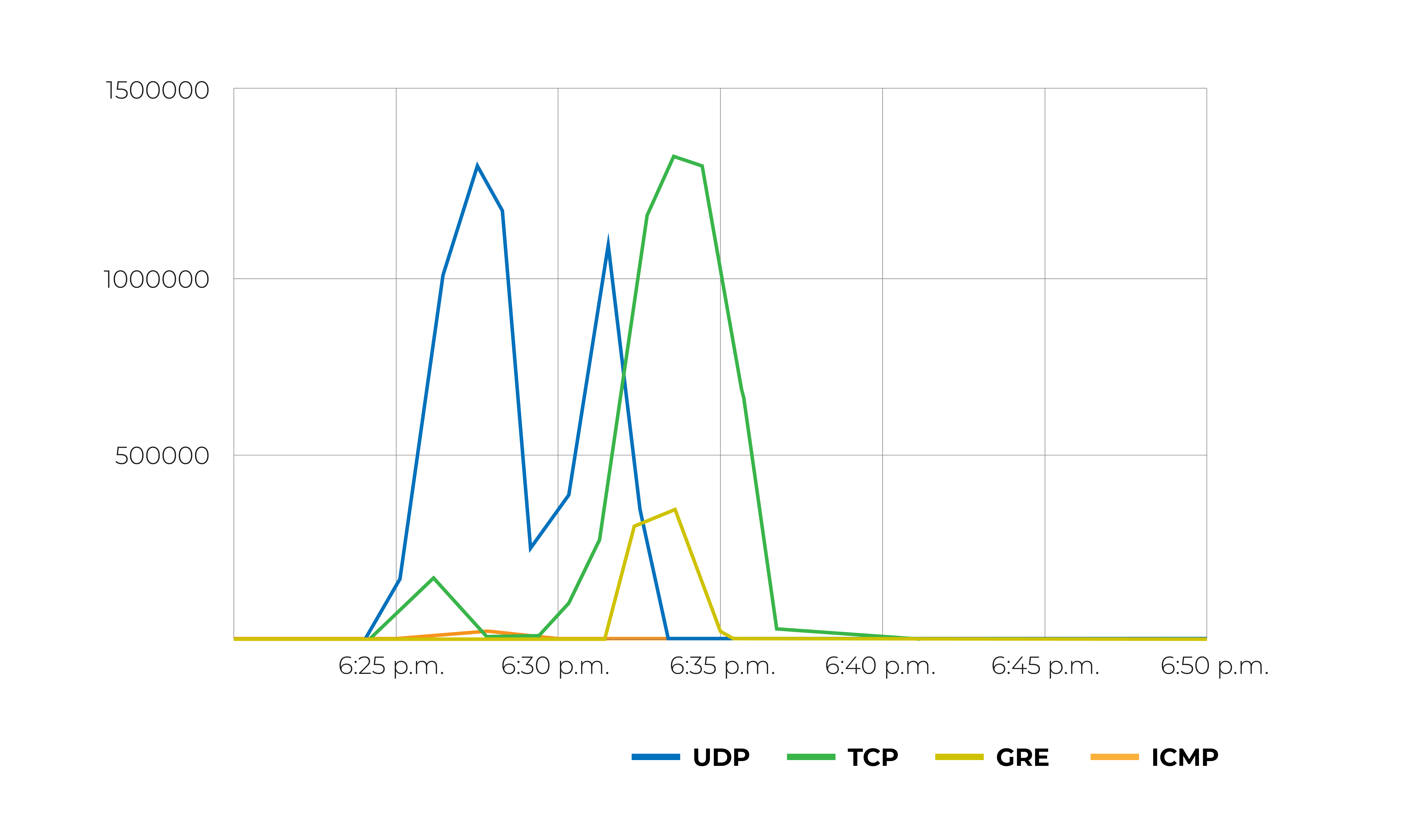
Attack Traffic in Mbps
Dynamics of attack strategies
The dynamics of the attack strategies were particularly noteworthy. After about four minutes, the packet size of the attacks was significantly reduced. This is a tactical variation that cybercriminals often use to circumvent defenses. The subsequent increase in packet size for the TCP and UDP vectors and the moderate adjustment for GRE prove that the attackers are adapting their strategies in real time to the defenses of Link11.
Such a complex attack scenario can inevitably overload the target’s network capacity and server CPU. A successful attack would have brought digital business operations to a complete standstill. This would have had catastrophic consequences for many companies. The course of the attack clearly shows that DDoS defense strategies must be continuously optimized and adapted to changing threats.
Simple but effective attack strategies
The simplicity of the methods used – illegitimate web-based traffic connections – proves that attackers still frequently target the most widely used Internet service protocols and ports. These types of attacks remain popular among cybercriminals despite more advanced methods, because they are easy to generate. The attackers know full well that many target systems do not have the necessary capacity to deal with such attacks.
The strategic targeting of home ISP providers and the associated access/eyeball networks also shows how attackers exploit vulnerabilities on the internet. By infiltrating such networks, they can generate mass traffic that is usually difficult to identify and block.
Are you looking to enhance your resilience to cyber attacks? Our experts are available to provide guidance on how to optimise your IT security. Contact us for a solution tailored to your specific needs.
IoT devices and vulnerabilities – a dangerous combination
The increasing networking of devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) have changed the threat landscape.
Many devices are vulnerable to attacks because they operate without security measures. The attacks prove that we need to improve security standards. The recently discovered vulnerability CVE-2024-3080 illustrates the need to improve security standards in the IoT industry.
It occurs in certain ASUS router models. The “authentication bypass” vulnerability allows attackers to gain access to routers without entering valid credentials. Normally, access to a router’s configuration interface requires entering a username and password. However, this vulnerability allows attackers to bypass the authentication process. A compromised router becomes part of a botnet and is used to carry out DDoS attacks. This highlights the dangers associated with unsecured IoT devices.
Effective defense through global scrubbing centers
To counter such an attack, flexible defense mechanisms are essential. Link11 was able to fend off the attack thanks to its global network.
Each scrubbing center was able to analyze data streams and filter out malicious data. The scrubbing centers in Europe took on a large part. Distributing the data across different locations effectively spread the load. Link11’s automated filters and adaptive algorithms were key. Thanks to AI, we were able to block illegitimate traffic while continuing to process legitimate requests. This allowed us to carry out the defense without human intervention and without affecting the customer’s systems.
Conclusion
In an era when the threat of cyberattacks is constantly growing, organizations should implement robust, scalable, automated DDoS defenses to protect themselves from cyberthreats.
Automated systems are essential to detect and neutralize attacks in real time. The complexity and dynamics of today’s attacks require intelligent solutions based on machine learning that can adapt to new threats.
Employees and users must be trained in the use of IoT devices and made aware of the dangers. In addition, best security practices and regular updates are essential to close vulnerabilities and reduce attack vectors. Companies need to take action and arm themselves against the growing threats in cyberspace.